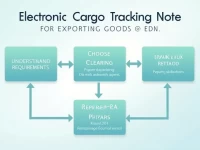
How to Accurately Complete the Dangerous Goods Application Form to Ensure Smooth Export
In the process of exporting dangerous goods, accurately filling out the dangerous goods application form is crucial. This form requires information such as the shipper and consignee, loading and unloading ports, container type, proper shipping name, classification, UN code, packaging category, and cargo weight. Special attention should be paid to the accuracy of flashpoint and packaging information to avoid affecting the shipping company's space arrangements.