In today's globalized economy, international money transfers have become increasingly common. Ensuring these cross-border transactions are completed successfully requires understanding one crucial element: SWIFT/BIC codes. These codes serve as the foundation of international payment systems, enabling banks and financial institutions to accurately identify each other and route funds to their intended destinations.
Understanding SWIFT/BIC Code Structure
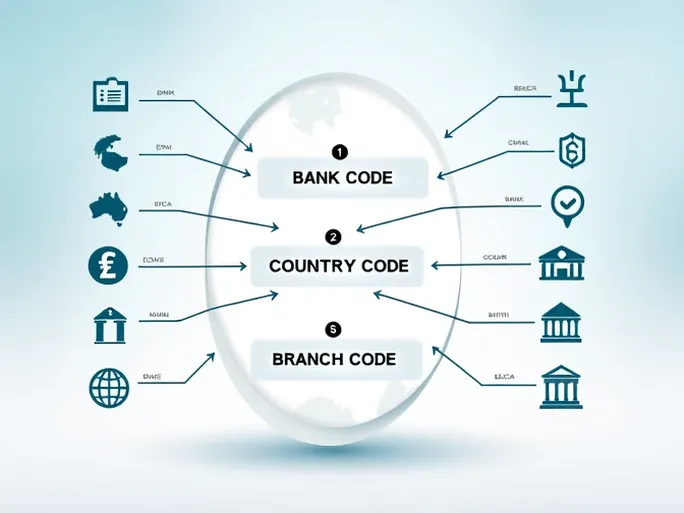
A SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) or BIC (Bank Identifier Code) typically consists of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters. The first four characters represent the bank code, followed by two characters indicating the country, and then two optional characters identifying the location or branch. This standardized structure minimizes errors and improves efficiency in international transactions.
Take MBANK S.A. in Poland as an example. Formerly known as BRE BANK S.A., this popular Polish bank uses the SWIFT/BIC code BREXPLPW BIA for international transfers:
- First four characters (BREX): The unique bank identifier corresponding to MBANK S.A.
- Next two characters (PL): Country code for Poland
- Final characters (PWBIA): Identifies the bank's specific branch in Białystok
Why SWIFT/BIC Codes Matter
These codes serve several critical functions in international banking:
Security: The SWIFT network enables banks to securely exchange payment information, significantly reducing fraud risks and providing peace of mind for both financial institutions and customers.
Speed: Transactions using SWIFT/BIC codes often complete within the same business day, sometimes within hours. This efficiency is particularly valuable for time-sensitive payments and commercial transactions.
Accuracy: The standardized format ensures funds reach the correct institution and specific branch, preventing misdirected payments.
Best Practices for International Transfers
When initiating an international transfer, consider these recommendations:
First, verify the SWIFT/BIC code directly with the recipient's bank. Financial institutions may change codes due to mergers, rebranding, or operational restructuring. Using outdated information could delay or misdirect your transfer.
Second, confirm all transaction details with the recipient. Different banking systems and country-specific requirements may necessitate additional verification steps.
Note that not all transactions require SWIFT/BIC codes. Domestic transfers or certain small-value international payments might use alternative systems. Always check with your bank for specific requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding SWIFT/BIC codes like MBANK S.A.'s BREXPLPW BIA is essential for secure and efficient international money transfers. By familiarizing yourself with these codes' structure and function, and by carefully verifying transaction details, you can confidently navigate global financial transactions. This knowledge becomes increasingly valuable as cross-border economic activity continues to grow.